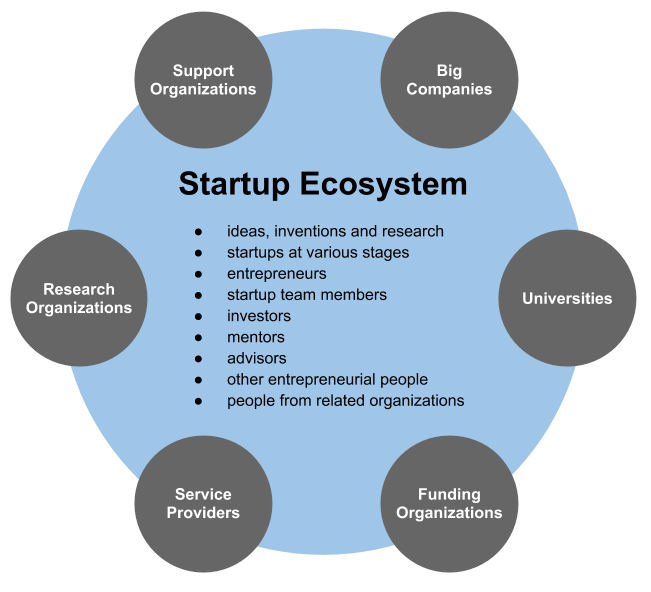
Understanding Michigan’s Entrepreneurial Ecosystem
To scale innovation and entrepreneurship, a system of management is applied to the whole entrepreneurial start-up ecosystem (rather than just single start-ups or organizations). Globally this is referred to as Start-up Ecosystem Management. In Michigan this role is handled by the Michigan Economic Development Corporation (MEDC).
Now that we are firmly entrenched into a global economy, there have been several independent studies made in various countries to evaluate start-up ecosystems. This analysis provides a baseline of understanding which enables comparison of various start-up ecosystems. Valuable insights of the strengths and weaknesses of different start-up ecosystems are then studied. According to these studies, the purpose of Entrepreneurial Ecosystem Management is to manage areas at various scales in such a way that ecosystem services and resources are preserved while appropriate resource use and options for livelihood are sustained.
Due to the nature of the start-up ecosystem management including the capability of catering needs for ecosystem management on a long term bases with its own sustainability through turmoil and disruptions, the responsibility is typically shared between those with such abilities.
Sustainability, Disturbance and Changes of an Entrepreneurial Ecosystem
A fundamental principle is the long-term good production sustainability for start-ups by the ecosystem. Sustainability is a precondition for entrepreneurial ecosystem management; it is not an afterthought. It also requires clear goals regarding future trajectories and behaviors of the system being managed. Other important requirements include a sound understanding of the system( including connectedness, people and organization dynamics) and the context in which the system is operating. An understanding of the role of people, talent and money as components of the ecosystems are also critical to the management team’s ability to sustain the ecosystem.
Since start-up ecosystems are dynamic entities—invariably, they are subject to periodic disturbances. Disturbance plays an important role in startup ecological processes. Much like start-up’s, when a startup ecosystem is subject to some sort of perturbation, it responds by moving away from its initial state. The tendency of a system to remain close to its equilibrium state, despite that disturbance, is termed its resistance. On the other hand, the speed with which it returns to its initial state after disturbance is called its resilience. The frequency and severity of disturbances determine the way they impact in the start-up ecosystem functions.
Major disturbances like a startup bubble burst leave behind an investment dry environment.
Startup ecosystems that experience severing disturbances undergo primary succession.
Less severe disturbances like individual start-up failures or support organization reorganization result in secondary succession.
More severe and frequent disturbances result in longer recovery times. Start-up ecosystems recover more quickly from less severe disturbance events.
From one year to another, ecosystems experience changes in their people, organizations and environments. Financial turmoil constitutes short-term variability in environmental conditions. The pool of people resources also vary from year to year, building up during downturn for bigger companies and crashing as they gear up their recruiting. Longer-term changes also shape ecosystem processes—where the biggest startup companies eventually make big exists releasing capital and talent to the start-up ecosystem.
Contact Nanokore’s Team of Experienced Entrepreneurs to schedule a free consultation regarding gaining a deeper understanding of Michigan’s Entrepreneurial Ecosystem.
Michigan’s Ecosystem Highlights
Topics Include:
✔ Four areas of Economic Development: Retention, Expansion, Recruitment and Start-Up
✔ The roles of Incubators (hatching) vs Accelerators (bringing up to speed)
✔ Michigan’s Legislative Act 57 of 2019
✔ Twenty one Michigan Smartzones
✔ The role of Michigan’s Small Business Development Center (SBDC)
✔ MEDC Strategy
✔ White papers and other global, national and Michigan data
Who is this information for and what are the benefits?:
✔ Ecosystem professionals looking to gain a broader view of Michigan’s Entrepreneurial Ecosystem
✔ Angel Groups and VC’s looking to gain insights into Michigan’s Entrepreneurial Ecosystem
✔ City, county and state employees
✔ Entrepreneurs looking to navigate and leverage Michigan’s
✔ Persons otherwise working on their Professional Certificate in Entrepreneurialism (PCE) from an accredited school
Nanokore is a member of Startup Commons. Startup Commons mission is to scale innovation and entrepreneurship by empowering ecosystem development with shared global knowledge.